Fair Trade coffee is coffee that’s certified to meet strict ethical, social, and environmental standards. It ensures farmers receive fair wages, work in safe conditions, and benefit from community development funds, promoting sustainability across the supply chain.

Fair Trade coffee is a movement that protects farmers, the environment, and your morning cup of coffee. With 75% of consumers trusting the Fair Trade Certified label [1], it’s clear that ethical sourcing matters more than ever. But what does Fair Trade coffee really mean, and how does it benefit both producers and drinkers? In this guide, I’ll discuss how coffee earns Fair Trade certification, why it’s important, and how it shapes a more sustainable coffee industry.
How Coffee Becomes Fair Trade Certified?
Becoming Fair Trade certified is not easy—and that’s a good thing. It ensures that every step of the coffee supply chain meets high ethical and environmental standards.
To start the process, a coffee cooperative, farm, or producer group must apply to a recognized certifying body. Two major certifiers are Fairtrade International and Fair Trade USA.

Once they apply, the journey begins. Here’s how coffee becomes Fair Trade certified, step by step:
1. Meeting the Standards
Coffee producers must follow strict social, economic, and environmental rules. These are designed to protect both people and the planet. Let’s break them down:
- Fair Prices: Farmers receive a minimum price that covers sustainable production costs.
- Community Development: A premium is paid to invest in local projects like schools and clinics.
- Environmental Protection: Practices that promote biodiversity and reduce harmful chemicals are encouraged.
2. Undergoing Audits and Inspections
After applying for Fair Trade certification, the farm or cooperative goes through a detailed inspection process conducted by a third-party auditor. This includes on-site visits where auditors observe farming practices, working conditions, and environmental efforts firsthand. They also interview workers and cooperative leaders to ensure fair treatment, safe working conditions, and adherence to ethical labor standards.
When the group passes, they receive the Fair Trade certificate. But this isn’t a one-time approval—ongoing audits and regular inspections are conducted to make sure the group continues to meet the criteria year after year.
3. Ongoing Monitoring
Fair Trade certification is reviewed annually. Every certified group must continue to meet the standards. Audits happen regularly to make sure:
- Workers are still paid fairly.
- Environmental rules are being followed.
- Community funds are used responsibly.
When any rule is broken, the certification can be suspended or removed.
What does the Fair Trade Label mean?
The Fair Trade label ensures that coffee is ethically sourced, guaranteeing fair wages and safe working conditions for workers. It also promotes environmentally sustainable farming practices and supports local communities through development premiums.
By choosing products with this label, you’re contributing to a more equitable global trade system.
How to ensure that the coffee is fair trade?
Look for certification labels from organizations like Fairtrade International or Fair Trade USA on the packaging. This way, you can be certain they’re actually certified!
Here’s how the fair trade coffee label looks like.

What’s the significance of Fair Trade Coffee Certification?
Fair Trade coffee certification plays a powerful role in improving the lives of farmers and strengthening global supply chains.
Economic Stability
Fair Trade certification offers economic stability by guaranteeing farmers a minimum price for their coffee. This protects them from unpredictable drops in the global market. When coffee prices fall, certified farmers still receive enough to cover the basic costs of sustainable production. This helps them continue farming without falling into debt or poverty.
Empower Farmers
It also empowers farmers by giving them a stronger voice in the supply chain. Many join cooperatives where they participate in decision-making, manage their own businesses, and access training to improve quality and yields. This sense of ownership helps build long-term success rather than dependence on outside aid.
Social Development
The certification also supports social development. In addition to the sale price, buyers pay a Fair Trade premium. This extra amount is invested back into the community, often used to build schools, fund healthcare services, and improve local infrastructure. In 2021 alone, Fair Trade coffee partnerships generated $31 million in community development funds, directly supporting education, clean water projects, and healthcare access for thousands of families [2].
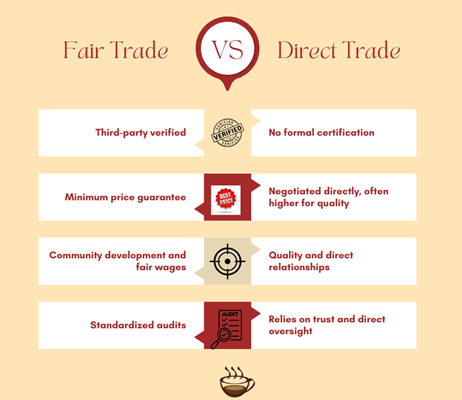
What’s the Difference between Fair Trade and Direct Trade Coffee?
Fair Trade coffee is certified by third-party organizations, such as Fairtrade International or Fair Trade USA. Direct Trade, on the other hand, skips third-party certification. Roasters work directly with farmers or cooperatives, often paying higher prices for exceptional quality.
Direct Trade model promotes close, long-term relationships between growers and buyers. While it allows more flexibility and usually leads to better bean quality, it doesn’t have the same standardized protections or audits as Fair Trade. Instead, it relies on mutual trust, transparency, and the buyer’s ethical standards.
Why is Fair Trade Important?
Fair Trade matters because coffee is a highly volatile commodity where prices can swing dramatically, leaving farmers struggling with unpredictable income. Climate change makes things worse with extreme weather events that destroy crops and reduce yields unpredictably.
Many coffee producers face huge barriers to accessing the capital they need to improve the quality of their farms and compete in the global market.
Fair Trade certification guarantees farmers receive minimum prices above market rates and provides premiums they can invest back into their communities and farming operations. This system creates stability in an otherwise chaotic market and helps small-scale farmers build sustainable businesses instead of just surviving harvest to harvest.
What are the challenges in Fair Trade Coffee?
Despite its benefits, Fair Trade faces several challenges:
- Quality can suffer: Farmers sometimes sell lower-grade beans under the Fair Trade label to make the most money.
- Complex certification process: Expensive and difficult requirements make it hard for many small farmers to qualify or maintain their Fair Trade status
- Exclusivity problems: Only small cooperative farmers qualify, excluding estate farms and other producers who might already provide fair wages and good conditions
- Not all farmers benefit equally: Co-ops get the premiums, but individual farmers may not see direct payouts.
Addressing these issues is important for the long-term success of Fair Trade initiatives [3].
What are some top Fair Trade Coffee brands?
Here are five well-known Fair Trade coffee brands that are committed to ethical sourcing, sustainability, and empowering farmers:
1. Allegro Coffee
Allegro Coffee was founded in Boulder, Colorado in 1977 and became one of the first certified organic roasters in the United States. The company built its reputation on bringing social integrity and ecological conscientiousness to specialty coffee markets, offering certified Organic, Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, and bird-friendly blends.
Their popular product lineup includes organic blends like Breakfast Blend, Early Bird Blend, and Espresso Sierra, all maintaining third-party certifications.
2. Kicking Horse Coffee
Kicking Horse Coffee is a Canadian roaster based in the Rocky Mountains that’s built its reputation on being “deep, dark & delicious” while maintaining 100% organic and Fairtrade certification across all their blends.
Their popular lineup includes bold roasts like Grizzly Claw (their strongest dark roast), Kick Ass (a medium-dark blend), Smart Ass (medium roast), and Three Sisters (medium blend) – all carrying both organic and Fairtrade labels.
3. Rise Up Coffee
Rise Up Coffee is a top Fair Trade and Organic coffee brand based in Maryland, known for its small-batch roasting and bold commitment to sustainability. The company believes the farmers who grow their coffee deserve the glory, which drives their dedication to fair trade practices that ensure growers receive proper compensation for their beautiful beans.
From its humble start as a coffee trailer in 2005, Rise Up has grown into a nationally recognized name with cafes, online sales, and wholesale partners. All their coffees—like House Roast, Breakfast, Espresso, and French Roast—are certified Organic and Fair Trade.
4. Cafédirect
Cafédirect is based in the UK and is one of the pioneers of Fair Trade coffee. They reinvest 50% of their profits back into the farming communities from which they source [4]. Their direct support helps improve livelihoods, fund local development, and build long-term partnerships.
They’re particularly famous for their single-origin coffees including Machu Picchu from Peru’s high-altitude Andes (rich, full-bodied with dark chocolate notes), Mount Kilimanjaro from Tanzania’s fertile slopes (bright and sweet with vanilla hints), and Colombia Reserva from Huila’s perfect micro-climates (smooth and rich with milk chocolate flavors). They also offer delicious blends like Mayan Gold and a range of instant, ground, and coffee bag options.
5. Mount Hagen
Mount Hagen Coffee stands as the world’s first instant coffee producer to achieve both organic and Fair Trade certification.
Their product lineup includes Regular Coffee, Decaf Coffee, and Organic Instant Espresso Coffee, all made from 100% Arabica beans sourced from Papua New Guinea. These are available in recyclable glass jars, resealable pouches, and convenient single-serve sticks.
Smooth, rich, and sustainably made, Mount Hagen proves that instant coffee can be both delicious and responsible.
What are some standard coffee certifications?
Here are some common coffee certifications other than Fair Trade:
Rainforest Alliance: Focuses on environmental conservation, wildlife protection, and improving working conditions.
Organic: Ensures coffee is grown without synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or chemical fertilizers.
Bird Friendly: Ensures shade-grown coffee that preserves bird habitats and maintains forest canopy coverage.
UTZ Certified: Focuses on sustainable farming and traceability throughout the supply chain.
Each certification has specific criteria, so choose one that aligns with your values and priorities.

Check out Related Articles:
- What is Organic Coffee
- What is Single Origin Coffee
- What is 3rd Wave Coffee
- Washed vs Natural Coffee
- What is Fermented Coffee
FAQs
Is fair trade coffee more expensive?
Yes, Fair Trade coffee often costs more than regular coffee due to the premiums paid to farmers and investments in community development.
Is Starbucks coffee fair trade?
No, Starbucks coffee is not Fairtrade certified. Instead, they use their own ethical sourcing program called C.A.F.E. (Coffee and Farmer Equity) program. It focuses on quality, sustainability, and fair treatment of farmers, but it’s not the same as third-party Fairtrade certification.
is fair trade coffee Organic?
Fairtrade coffee isn’t always organic, but some of it is. Many Fairtrade-certified farms also meet organic standards, like those used by Kicking Horse Coffee or Rise Up Coffee. But being Fairtrade doesn’t automatically mean the coffee is organic.
References:
- https://www.fairtrade.net/en/for-business/benefits-of-being-certified/consumer-trends
- https://www.fairtradecertified.org/what-we-do/what-we-certify/coffee/
- https://ssir.org/articles/entry/the_problem_with_fair_trade_coffee
- https://www.cafedirect.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/2020-Cafedirect-Annual-Review-2019_FINAL-HR.pdf



